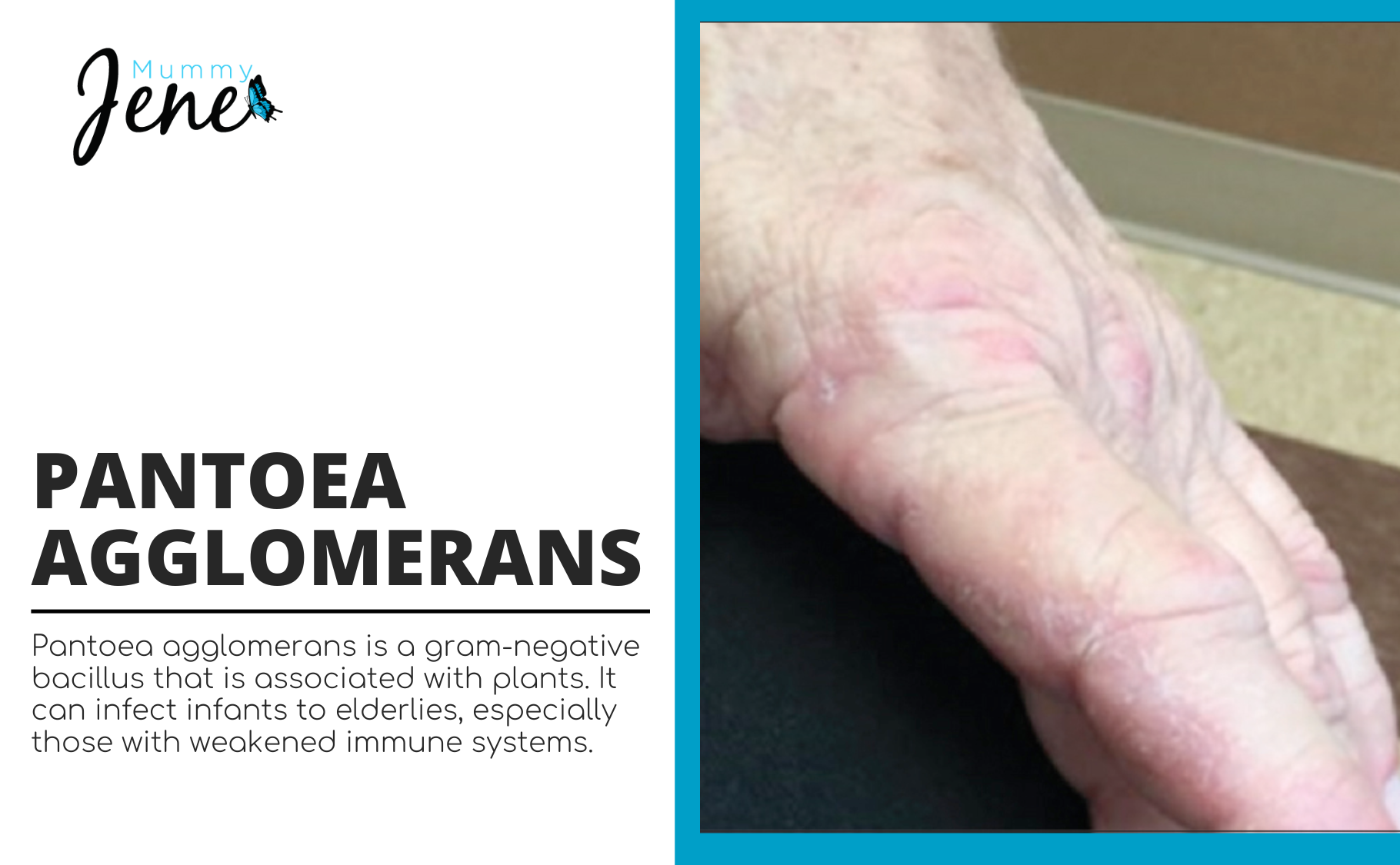
Pantoea agglomerans previously known as Enterobacter agglomerans is a gram-negative bacillus that belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Pantoea agglomerans has beneficial roles in antibiotic production as an immune potentiator in cancer patients. It is also helpful for biopesticide and food preservation. It is the common cause of infections and at the same time, it is a rare cause of opportunistic infections from wound infection. This infection is usually acquired from contaminated medical equipment, contaminated fluids, and plants.
Who Are At High Risk Of This Infection?
Since this infection can penetrate deep into the bones and bloodstream, it can be life-threatening if not treated immediately and correctly. Individuals who are at high risk of getting pantoea agglomerans infections are those patients after surgery, those who have pneumonia, or in other words, those who are immunocompromised, or those with weakened immune systems. It is diagnosed through positive cultures from specimens such as; blood, pus, urine, and central venous line sample.
What Causes Pantoea Agglomerans?
Based on clinical outcomes, these are the significant causes of infection that lead to bacteremia outbreaks.
- Exposure to contaminated medical equipments
- Exposure to contaminated intravenous fluids; example patients receiving hemodialysis and blood transfusion for adults, and intravenous hydration or contaminated powdered milk for infants
- Ingestion of fruits and vegetables with pantoea agglomerans
- Wound infection from plant thorn, or open wounds in contact with plant residing bacteria
- Patients with GERD and untreated viral hepatitis are associated with a high rate of bacteremia.
Signs And Symptoms
- Fever
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Change in blood cell count
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Hypotension
- Shock
Treatments
Patients with infections caused by pantoea agglomerans can be treated successfully with the right antibiotics. Below are the antibiotics used with a 100% rate of effectiveness.
- Cefotaxime
- Gentamicin
- Cefotaxime
- Ampicillin
- Fosfomycin
- Imipenem
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ceftazidime
The treatment caused by polymyxin B-immobilized has a 100% effectivity rate. This procedure removes lipopolysaccharide from gram-negative organisms. In most adult cases, related diseases or infections caused by pantoea agglomerans are usually mild. However, it can lead to septicemia, multiple organ failure, and even death for infants and pediatric patients. Most patients started with wound superinfection and mostly occured in a medical environment. As mentioned, it is also from food, plants, or even in your garden. When you think you are not feeling right and experiencing some symptoms, see your doctor for immediate diagnosis and treatment.